Why Export Baselines?
Before you apply patches or extensions to ESX/ESXi hosts, you might want to test the patches and extensions by applying them to hosts in a test environment. You can then use Update Manager PowerCLI to export the tested baselines to another Update Manager server instance and apply the patches and extensions to the other hosts.
Workflow
This workflow describes how to test patches by using one Update Manager instance and how to export the patch baseline containing the tested patches to another Update Manager instance.
Pages are referenced from Installing and Administering VMware vSphere Update Manager
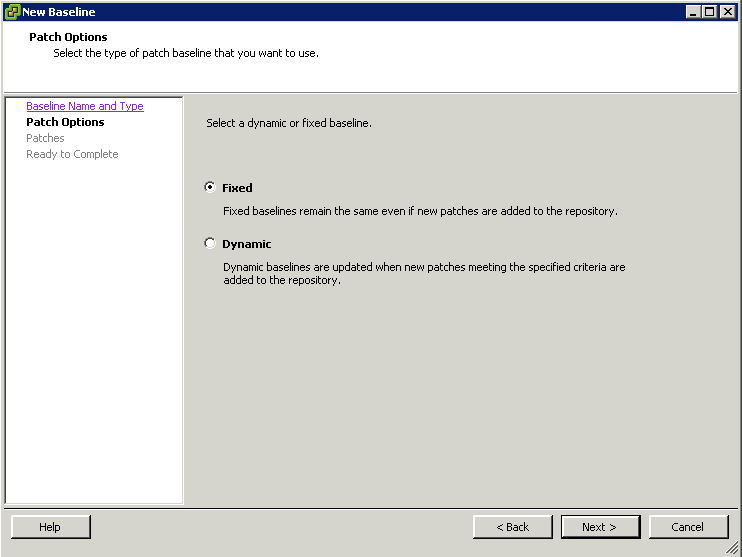
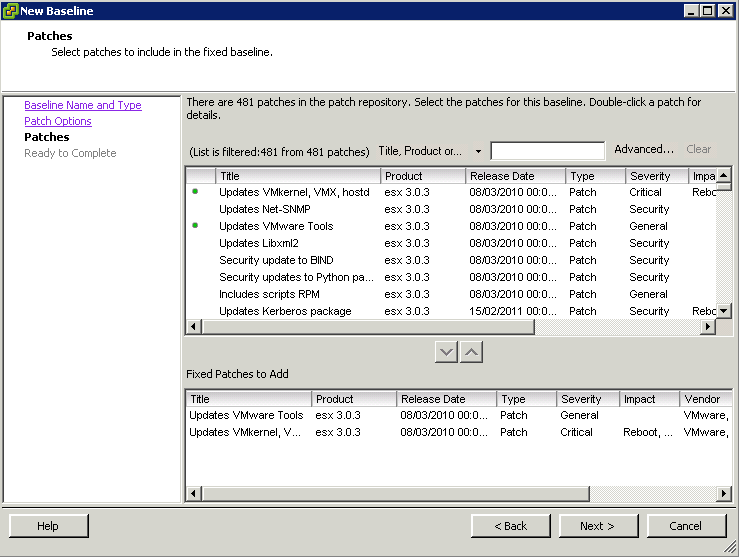
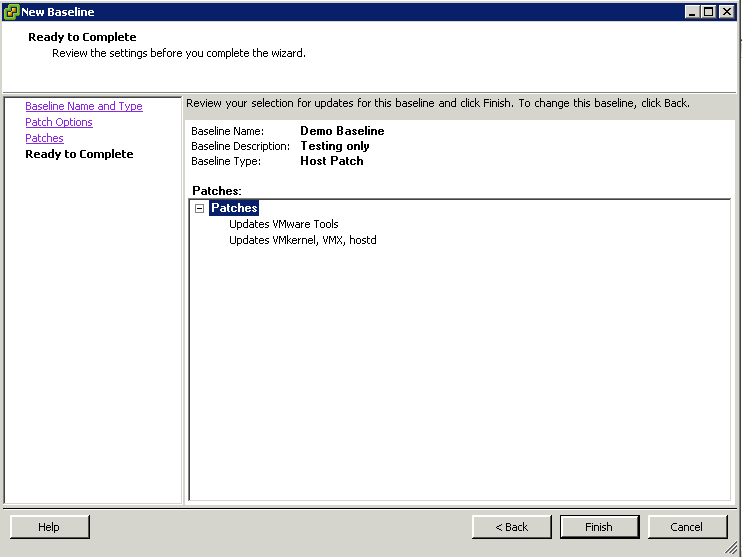
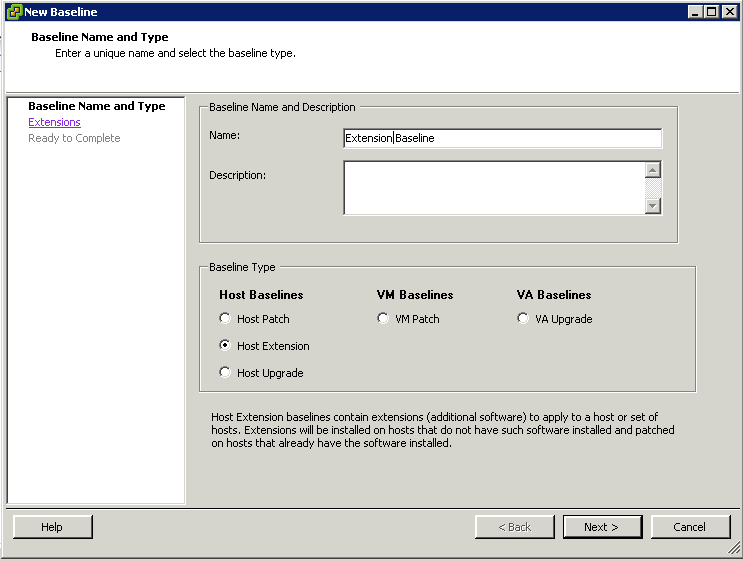
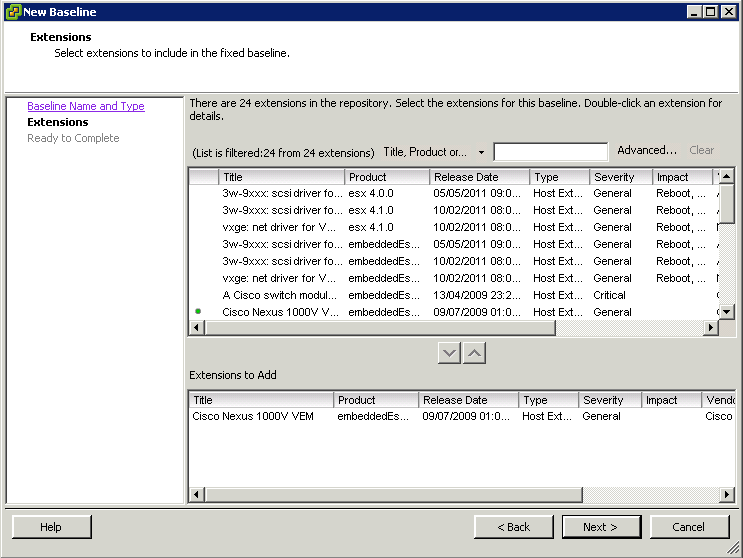
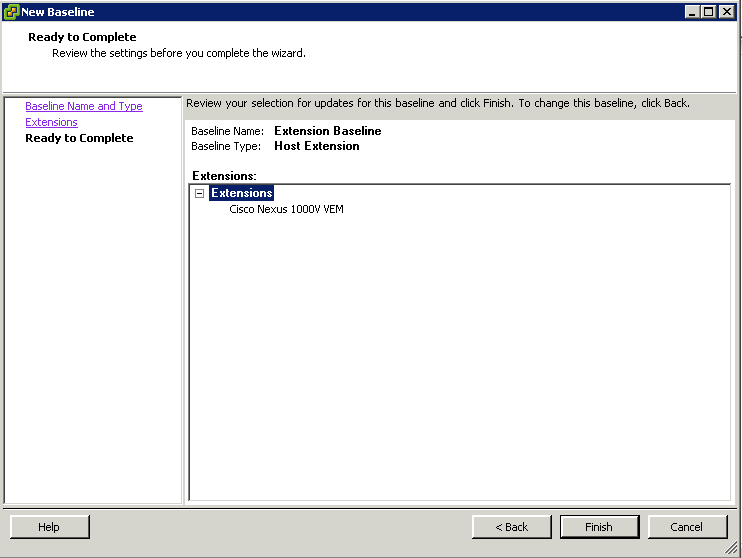
- Create fixed host patch baselines.
Create fixed patch baselines containing the patches that you want to test. Fixed patch baselines do not change their content when new patches are downloaded into the Update Manager patch repository. You can create a fixed patch baseline from the Baselines and Groups tab of the Update Manager Administration view. For more information and a detailed procedure, see “Create a Fixed Patch Baseline,” on page 85.
- Attach the patch baselines to a container object containing the hosts that you want to scan or remediate.
The container object can be a folder, cluster, or datacenter. You can attach baselines and baseline groups to objects from the Update Manager Compliance view. For more information about attaching baselines and baseline groups to vSphere objects, see “Attach Baselines and Baseline Groups to Objects,” on page 97.
- Scan the container object.
After you attach baselines to the selected container object, you must scan it to view the compliance state of the hosts in the container. You can scan selected objects manually to start the scanning immediately. For detailed instructions on how to scan your hosts manually, see “Manually Initiate a Scan of ESX/ESXi Hosts,” on page 101. You can also scan the hosts in the container object at a time convenient for you by scheduling a scan task. For more information and detailed instructions about scheduling a scan, see “Schedule a Scan,” on page 102.
- Review the scan results displayed in the Update Manager Client Compliance view.
For a detailed procedure about viewing scan results and for more information about compliance states, see “Viewing Scan Results and Compliance States for vSphere Objects,” on page 103.
- (Optional) Stage the patches in the attached baselines to the hosts that you want to update.
You can stage the patches and copy them from the Update Manager server to the hosts before applying them. Staging patches speeds up the remediation process and helps minimize host downtime during remediation. For a detailed procedure about staging patches and extensions to hosts, see “Stage Patches and Extensions to ESX/ESXi Hosts,” on page 121.
- Remediate the container object.
Remediate the hosts that are in Non-Compliant state to make them compliant with the attached baselines. For more information about remediating hosts against patch or extension baselines, see “Remediate Hosts
- Export the patch baselines from the Update Manager server that you used to test the patches, and import them to another Update Manager server.
You can export and import patch baselines from one Update Manager server to another by using an Update Manager PowerCLI script. The example script on Page 156 of Installing and Administering VMware vSphere Update Manager creates a duplicate of the baseline MyBaseline on the $destinationServer.
The script works for fixed and dynamic patch baselines as well as for extension baselines.